The IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME) has been held in Brisbane, Australia, from July 10 to 14, 2023. ICME is a Class B conference recommended by CCF, and one of the high-level international conferences in the field of multimedia. It is also an important academic forum for showcasing and exchanging scientific achievements and innovative projects in the field of multimedia. This year, ICME 2023 has a total of 1415 valid submission papers, with an acceptance rate of approximately 28%. After multiple rounds of rigorous selection, only two papers were awarded: Best Student Paper and Best Student Paper Runner Up. Zhou Huayi, a doctoral student in the computer science department, presented a paper titled "Body Part Joint Detection and Association via Extended Object Representation", which was selected from 12 candidate papers and won the runner up for the Best Student Paper Award at the conference through comprehensive evaluation by the paper review committee and conference judges, paper review, presentation and defense. The first author of the paper is Zhou Huayi, a 2020 doctoral student, and the supervisor is Lu Hongtao. This paper was completed in cooperation with East China Normal University.

Research Background:
In recent years, computer vision has made rapid progress with the assistance of deep learning, especially in the field of object detection, where various advanced methods have performed outstandingly. The same applies to the detection of the human body and various body parts (such as the face, hands, and head). Accurate detection of the human body and its parts can be used for crowd counting and pedestrian flow monitoring, as well as for various downstream tasks such as face recognition, human pose estimation, pedestrian re-id, or human-object interaction detection. However, most existing human body or any body part related detection methods are isolated, which makes the process of matching these body parts with the belonging human body much more complex and prone to errors in the later stage.
Paper Introduction:
The award-winning paper pioneered the research on the joint association and detection of the body and parts in response to the aforementioned issues. Unlike previous methods that require the establishment of additional association strategies or subnetworks, the paper proposes a direct extension of traditional object detection representations by encoding various body parts of the human body as offset points into the representation to achieve joint detection of the whole and parts. The method is named BPJDet. This simple yet efficient approach can be combined with a single stage object detection framework to achieve end-to-end trainability, saving training time and omitting various error prone post-processing operations. It achieves the best performance on multiple joint detection datasets of body and parts. Most importantly, this concise approach can continue to provide support for other downstream tasks, such as precise crowd head counting based on double-checking of the human body and head, or expanding detection representation vectors further to achieve hand contact state estimation between people and objects. The related works have been extended to journal article BPJDetPlus.
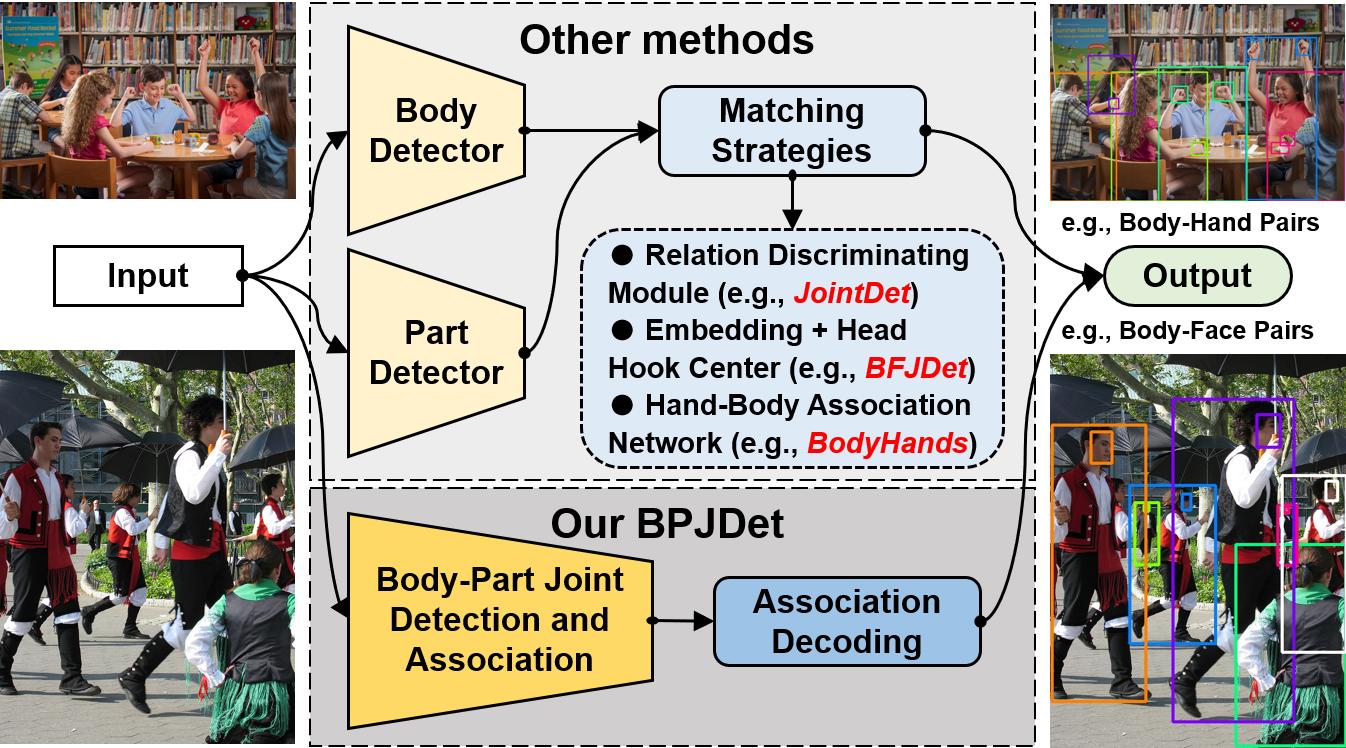
Illustrations of BPJDet and its comparison with other existing methods.
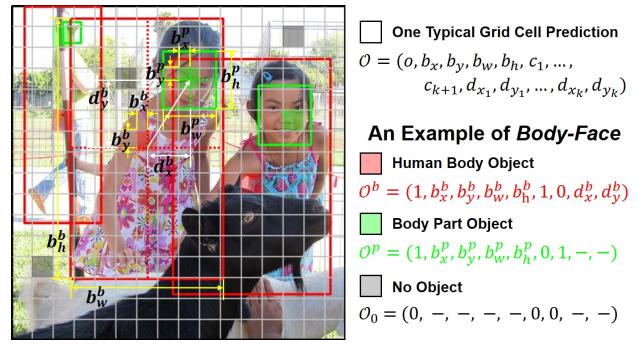
Example of the proposed extended object detection representation
(Demo of body-head joint detection using BPJDet)
BPJDet Code:https://github.com/hnuzhy/BPJDet
(Demo of body-parts joint detection using BPJDetPlus)
BPJDetPlus Code:https://github.com/hnuzhy/BPJDet/tree/BPJDetPlus