
Fig.1 The integration of Artificial Intelligence throughout the comprehensive scenario and course of diabetes management represents a significant advancement in healthcare technology. (cited from this review paper)
Diabetes, a major challenge in the global public health sector, is anticipated to expand from 529 million individuals in 2021 to a staggering 1.31 billion by 2050. Furthermore, the rising prevalence of pre-diabetes indicates that the global burden of diabetes may continue to escalate in the future. The inadequate management of diabetes in patients can drastically elevate their vulnerability to severe complications, including cardiovascular disease and amputations of the lower extremities. This critical scenario disproportionately impacts low- and middle-income countries, where nearly 80% of the world's diabetes patients reside. In addressing this challenge, the utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) in diabetes care is garnering considerable attention and scrutiny, with the objective of delivering personalized management and treatment modalities that are tailored to complex scenarios.

Fig. 2 The Review "Artificial Intelligence for Diabetes Care: Current and Future Prospects" published by The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology
On July 23 2024, the esteemed medical journal, The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology (https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/home), renowned in the realm of clinical, public health, and global health, released a review titled "Artificial Intelligence for Diabetes Care: Current and Future Prospects." (https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(24)00154-2) This review, authored collaboratively by Professor Bin Sheng from the Computer Science and Engineering Department of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Prof. Yih-Chung Tham from National University of Singapore, Prof. Huating Li from Shanghai Jiao Tong Univerity School of Medicine, and Prof. Lee-Ling Lim from University of Malaya, alongside scholars from various nations, marks a significant milestone in the journal's history and diabetes care. The review primarily delves into the utilization of artificial intelligence in diabetes care, emphasizing the advancements and immense potential of AI technology in the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes and chronic diseases, positioning it as a pivotal trend in global interdisciplinary research.
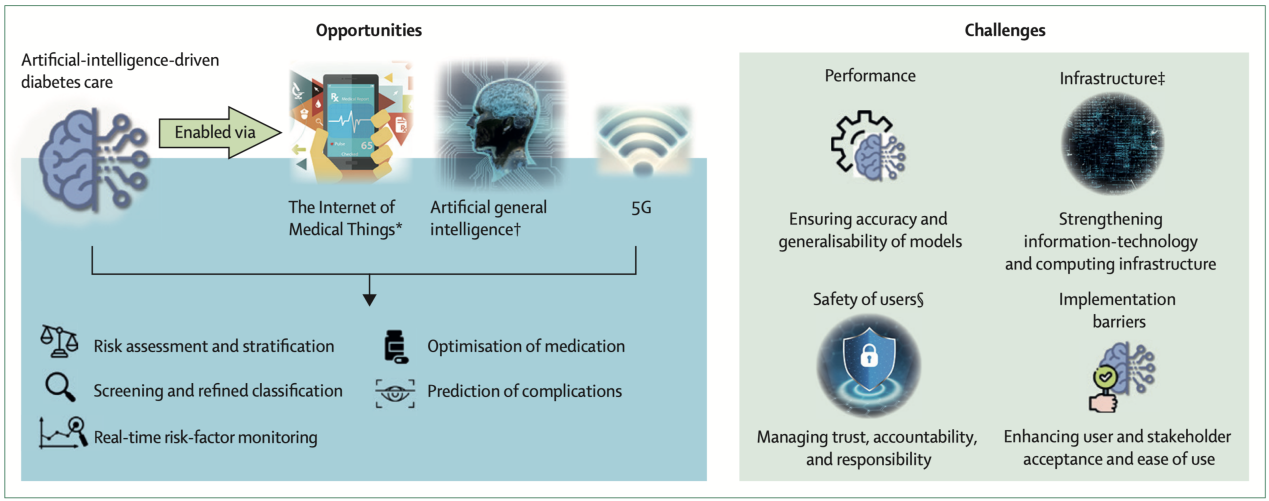
Figure 3: Analysis of the Prospects and Hurdles in the Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Diabetes Care Administration (cited from this review paper)
The development of an intelligent health management platform is crucial in enhancing patients' self-management capabilities. Leveraging continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology and reinforcement learning algorithms, AI-assisted diabetes management offers personalized insulin dosage recommendations, accurate predictions of diabetes complications, and real-time AI-driven clinical decision support for doctors and patients. This facilitates timely intervention, improves treatment outcomes, and enhances patients' quality of life. Furthermore, non-invasive, straightforward, and rapid diabetes screening methods, subtype classification systems, AI-based mobile health platforms, and remote monitoring systems contribute significantly to enhancing patients' self-management, optimizing medical nutrition therapy plans, enhancing insulin dosing accuracy, and ultimately improving diabetes control levels. Notably, the utilization of AI in screening and predicting diabetes-related complications, including retinopathy, kidney disease, peripheral neuropathy, and foot ulcers, coupled with early intervention and treatment, mitigates the impact of these complications on patients' quality of life.
However, it is imperative to address the challenges posed by the rapid advancement of AI technology, including bias mitigation, ethical considerations, and equity issues. Therefore, ensuring the inclusive and ethical development of AI is crucial to enhancing the efficacy of healthcare professionals and patients in disease management.